With sudden advancements, blockchain technology has developed a new identity in the enterprise. As companies face difficulties in data management and security, its technology permits for secure transactions to occur without the presence of a central authority.
It is important to note that this new form of emerging technology still remains in the experimental phase.
However, nowadays approximately 40 of the world’s top financial institutions and a large number of firms are playing with distributed ledger technology, permitting a digitally secure and transparent way to verify the ownership of assets. This could in turn speed up the rate in which transactions are executed, cut costs, as well as lower the risks of fraud.
The data structure that is blockchain allows for the production of a digital ledger of transactions that can be shared among a network of computers. Each node within the network has a copy of the entire ledger. Cryptography is used so that the participants are permitted to manipulate the ledger in a secure format in which a central authority is not needed.
Removing or changing data that is already existing on the blockchain ledger is difficult. Complex algorithms are used to verify and evaluate the proposed transaction. If a large number of nodes on the network determine it as being valid, than the transaction will be approved and consequently, a new block will be added to the chain.
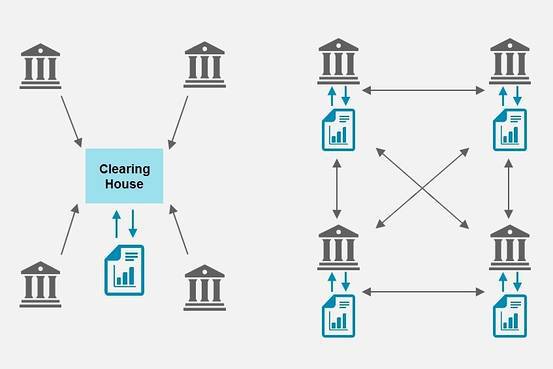
The main priority for blockchain technology is so to allow computers that share a common network to communicate without the need of a third party or middleman. This is proven to be extremely beneficial for financial institutions because the clearinghouse can be eliminated by providing each bank with a copy of the ledger.
There is obvious contradiction surrounding the security aspect of this new and emerging technology. However, it still remains an efficient way for networks to eliminate the central authority and communicate appropriately.
For more information on blockchain technology, click here.